A conceptual approach to implementation of data science in marketing
The research contains the results of the development of a conceptual approach for the implementation of Data Science into the marketing system. The approach describes the 5 stages of implementation of mathematical and statistical methods of analysis, machine learning technologies, and Data Science methodology to effectively solve different marketing tasks and increase business results.
Modern marketing is considered as a system of organization, production, and sale of goods based on comprehensive research of the market and real requests of potential consumers in order to obtain maximum profit and strengthen competitive advantages [1]. In order to structure the process of marketing activity, determine the most effective sequence of its implementation and direct all resources to the fulfillment of short-term and long-term goals of the activity, it is recommended to implement Data Science methodology in the enterprise. The use of Data Science capabilities contributes to making data-driven analytics central to marketing decision-making [2] by studying the main influencing factors on business and creating a decision-making support system [3].
The conceptual approach for working with data in the field of marketing consists of three parts: analysis of the problem situation and problem statement; direct data analysis and modeling using Data Science; formation of decisions and their implementation. The most valuable is the central unit with solution search and modeling. Below is a detailed description of each of the stages.
Stage 1 - Business and brand analysis. At this stage, it is very important to understand all the specifics of the business, and all the processes within the enterprise, which ultimately affect the formation of the target metric. It is necessary to make deep dive into the business, and the features of the product offered to the market and analyze the entire sales funnel to the smallest detail in order to understand each stage on the way to the formation of the target metric and determine all possible influencing factors.
Stage 2 - research and understanding of influencing factors, collection, and preparation of data for analysis and modeling. At this stage, it is relevant to understand what data is needed to build the model, what data is available on the business side, how it is formed, what it means, for what period it is available, and how it is collected.
The model is always built for a specific enterprise, and the sources of the most important data for target and influential parameters are confidential internal business data, market research data, as well as own research conducted by a team of analysts. This work usually takes from three to five weeks for research of medium complexity.
After collecting information, all data are compiled into a single database and prepared for analysis and modeling. Often, different data are stored in different formats. For high-quality processing, they must be standardized, that is, reduced to a single format. Data collection and preparation is one of the key steps in working with Data Science and can take 50-70% of the total time, reaching up to six months.
Stage 3 - data analysis and hypothesis formation. At this stage, it is necessary to conduct a detailed analysis of the market, its structure, the dynamics of positions and sales of the brand and its competitors, conduct an analysis of the target audience, competitive environment, the activity of brands in various media channels, and analyze the position of the brand in each element of the marketing complex. Such research will make it possible to form key conclusions and hypotheses, which will be further tested through the modeling of the marketing mix, as well as the application of other Data Science methods (for example, clustering or customer classification).
Stage 4 – models’ construction and testing. This is the most technical part of the research - directly the modeling stage, where business representatives experience difficulties in understanding all details, but it is necessary to trust an experienced team of data scientists to ensure the execution of all processes at a high level.
Model preparation is an interactive process. It is advisable to plan meetings and discuss issues and intermediate results with a working group consisting of company representatives because they know the category and the product at the highest level.
Various software are used to build models and analyze the results, the most popular of which are IBM SPSS Modeler, Loginom, Weka, E-Views, R-Studio (with R programming language), Python programming language, Microsoft Power BI, etc.
In general, this stage is one of the most difficult and can last up to two months. It is envisaged to build marketing mix models for each brand of the company, as well as models for competitors to find additional solutions based on successful cases of other players. In addition, on the basis of the built models, price elasticity is calculated and the optimal level of the price index is determined, the influence of factors on each other is quantified, and ROI is calculated in maximum detail by periods, formats, communication channels, etc. In parallel, clustering and classification models can be applied to customer data to solve the problems of minimizing outflow and maximizing the effectiveness of communication with the consumer. In addition, methods of finding association rules, Text Mining technologies for analyzing information about consumers and their relationship to the enterprise on the Internet (Social Listening research), as well as Big Data processing technologies can also be used to solve marketing problems. On the basis of the received information, there are confirmations or refutations of previously formed hypotheses and forming conclusions that will become the basis for managerial marketing decisions.
Stage 5 - development of solutions and recommendations, scenario forecasting, and model support. Constant work with the model is the basis of this stage. This is the most valuable part of modeling, as the model turns into a decision-making tool. The model is evaluated both from the point of view of statistical significance (technically) and from the point of view of compliance with business results (practically), scenario forecasting of business indicators is carried out under different plans regarding elements of the marketing complex and factors of the market environment.
The peculiarity of the modeling process is that after its completion, together with the results of the analysis and the decisions that follow from it, an information-analytical support system for making marketing decisions based on interactive dashboards can be developed.
Taking into account the processes that take place at each of the stages, an extended conceptual scheme for the implementation of modeling of marketing activity was proposed, presented in the Figure 1.
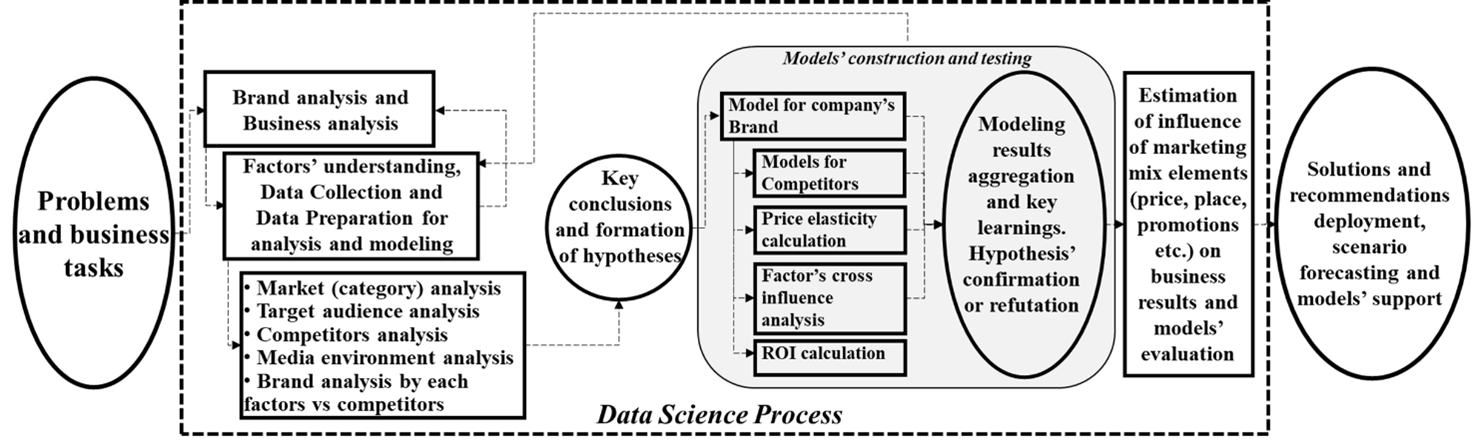
Using mathematical and statistical methods of analysis, machine learning technologies, and Data Science methodology, working with enterprise information, with data on media support for the brand, category, and a number of external factors allows not only to forecast results but also to plan their gradual achievement, including the rational involvement of communication channels and investment allocation that maximizes ROMI. As a result, there is a continuous optimization process to increase sales, and improve market positions by developing and creating effective marketing solutions for business development strategy.
References
- Alj, M., Illyas, M., & Rehman, C.A. (2016). Impact of Consumer Centric Marketing Mix Elements on Consumer Buying Behavior: An Empirical Investigation in Context of FMCG Industry of Pakistan. Kuwait Chapter of Arabian Journal of Business and Management Review, 5(5), 30-42. DOI: 10.12816/0019028.
- Johnson, D.S., Sihi, D., & Muzellec, L. (2021). Implementing Big Data Analytics in Marketing Departments: Mixing Organic and Administered Approaches to Increase Data-Driven Decision Making. Informatics, 8, 66. DOI: 10.3390/informatics8040066.
- Kengpol, A., Pichitkarnkar, T., & Elfvengren, K. (2022). A decision support system for consumer behavior of Chinese in-bound tourists on functional beverage: an empirical study during COVID-19 with Thailand sandbox. Applied Science and Engineering Progress, 15(1). DOI: 10.14416/j.asep.2021.09.001.