COMPARISON OF USING FUZZY LOGIC AND NEURO-FUZZY NETWORKS FOR MODELLING CORPORATE BANKRUPTCY RISK ESTIMATION
Klebanova T.S.
DrSc., Professor
t_kleb@ukr.net
Gvozdytskyi V.S.
Ph.D, Associate Professor
gvozdikramm@gmail.com
Simon Kuznets Kharkiv National University of Economics (Ukraine)
The bankruptcy of an individual entity has a number of negative consequences, each bankruptcy undermines the national economy, significantly hindering its development. In the current conditions, Ukraine has faced significant problems related to long-term political, financial, economic instability, which is why every day the number of insolvent businesses is increasing. In these conditions the first priority goal for the corporate’s management is to estimate the propensity of an individual enterprise to bankruptcy and to develop a crisis management system based on an analysis of the results of this estimation.
Most existing methods and models of bankruptcy diagnostics, as noted by economists [2-4], have significant drawbacks, primarily due to the inability to use them in the Ukrainian environment due to inadequate results. The peculiarity of these methods is the need for a clear specification of models, also the additional difficulty of using these methods creates the unsteadiness of the studied economic processes. Different types of intellectual systems have their own peculiarities, which makes them most suitable for solving certain classes of problems and less suitable for others.
But at the same time with technological progress, researchers have started to pay more attention to artificial intelligence, among them the most popular one are neural networks that have proven themselves well for object identification tasks, but at the same time they are very inconvenient to explain how they perform such identification. Systems with fuzzy logic, on the contrary, are practical for explaining their conclusions, but they cannot automatically acquire the knowledge to use them in output mechanisms. This reasoning formed the basis for the creation of fuzzy neural network apparatus, in which conclusions are drawn on the basis of fuzzy logic apparatus, but the corresponding membership functions are adjusted using neural network learning algorithms [3].
Fuzzy logic allows to formalize qualitative information from expert economists for a particular field of application, and to present a set of acquired knowledge in the form of a system of fuzzy rules of inference that allow you to analyze the conclusions obtained in the course of operation of the hybrid intellectual system [2].
Neural networks provide the ability to display algorithms of fuzzy inference in the structure of the neural network, entering in the information field of the neural network data received from expert economists. The knowledge base formed in such way is automatically adjusted in the course of training the neural network [5].
As described in [4], one of the first steps of the development of fuzzy logic model is create the rules for classification of the values of input factors of the model. After that, the rules of recognition of the financial state of the enterprise and the membership functions of belonging were formed. According to these rules, the model was tested in five enterprises: 3 bankrupt and 2 operating. So, it can be clearly concluded that the model at least does not produce contradictory results: the enterprise which will become bankrupt in the next reporting period is in unsatisfactory state (deep crisis), and the enterprises that are still operating are in a satisfactory state with membership functions equal 1 and 0.7 respectively. And the state of the enterprises that became bankrupt after some period, according to the model, is worse than the state of the existing ones. That is, this model can be used to adequately estimate the financial state of enterprises.
This fuzzy model was also used to estimate the financial state of the operating entity over 13 quarters. At present, the bankruptcy risk for this enterprise can be estimated as quite high, that is, the management of the enterprise is offered to develop a scheme of crisis management.
Hybrid neuro-fuzzy systems have found the largest scope among all possible methods for fuzzy sets and neural networks synthesis. This is due to the fact that they allow the fullest use of the strengths of fuzzy systems and neural networks. A characteristic of hybrid systems is that they can always be regarded as systems of fuzzy rules, and the tuning of membership functions in the preconditions and conclusions of rules based on the set of learning is done through neural networks. There are several hybrid systems architectures, each designed to solve its own range of problems. This creates some difficulties in the study and application of these systems [1].
Generated hybrid network structure is shown on Fig. 1.
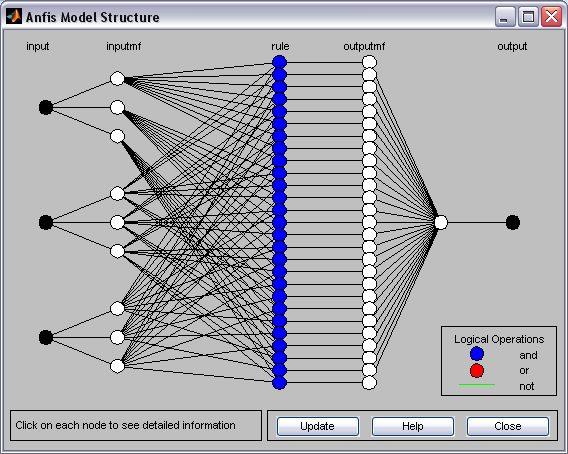
Fig. 1. Structure of the generated system of fuzzy output
For the reviewed example (model of bankruptcy risk estimation), the fuzzy output system contains three input variables with three terms each, 27 fuzzy rules, one output variable with 27 terms.
A total of 40 training cycles were selected. The greater the number, the greater the value of the average error in the model, but also increase the adequacy of the model. As we can see from Fig. 4, the error values depend only on the first four training cycles, after which they all equal about 6,789%. So, we can say about the high adequacy of the constructed neuro-fuzzy model [2].
As a result, it was determined that in the last studied period, an enterprise with a membership function of 0.6224 was on the verge of bankruptcy, that is, the risk of bankruptcy for this enterprise in the near future is high, which was confirmed by the previous model built as well.
Thus, in order to achieve the goal of identifying the real threat of bankruptcy of enterprises, the article used some of the most advanced methods that have already proven their adequacy: mathematical apparatus of fuzzy logic and neuro-fuzzy networks.
According to the simulation results, both methods confirmed approximately the same conclusions regarding the risk of bankruptcy of a particular enterprise. But, in our view, neuro-fuzzy models give more adequate results (the error of the constructed model was approximately 6.8%). When building neuro-fuzzy models by analogy with the previous method, one can also expertly associate specific intervals of the values of the obtained membership functions to particular classes of crisis. And the interpretation of the simulation results can be expanded in that way. This method takes into account the main disadvantages of other approaches, is adaptable to changing conditions, allows for a more flexible and quick response to the crisis. Therefore, it can be argued that the neural network tools can be effectively applied in many areas and, above all, in the economy.
REFERENCES
- Chung, K., Tan, S., Holdworth D. (2008) Insolvency Prediction Model Using Multivariate Discriminant Analysis and Artificial Neural Network for the Finance Industry in New Zealand. International Journal of Business and Management, 3(1), p. 19-29. Retrieved from Business Source Premier database.
- Klebanova T.S., Gvozdytskyi V.S. (2015) Estimation of the propensity of enterprises to bankruptcy on the basis of methods of fuzzy logic and fuzzy neural networks. Business Inform, №10, p. 165-170.
- Matviychuk A.V. (2010) Modelling financial stability of enterprises using the theory of fuzzy logic, neural networks and discriminant analysis. Visnyk of NAS of Ukraine, №9, p.24-46.
- Ponomarenko V. S., Raevneva E. V., Stepurina S. A. (2009) The mechanism of enterprise reorganization management: the basics of formation and implementation models. Kharkiv, INZHEK, 304 p.
- Zarei M., Rabiee M., Zanganeh T. (2011) Applying adaptive NeuroFuzzy model for bankruptcy prediction. International Journal of Computer Applications, 20(3), p. 15-21.